What is plaster?
Plaster is a common material used for decoration and building. It starts out as a fine powder and becomes a paste once water has been added. Plaster in its paste form is very malleable, and can be shaped into many forms. The paste dries quickly into a smooth hard finish. There are three common types of plaster - their difference lies in whether the powder is based on gypsum (or plaster of Paris), lime, or cement.
Why is plaster used?
Plaster was once widely used to create interior wall surfaces. Since the introduction of plasterboard however, this use for plaster has declined, as plasterboard is much easier to install. While plaster can be used to patch holes and cracks in existing plaster or plasterboard walls, its primary use is now for decorative interior mouldings. Mouldings such as skirting boards and dado rails are often installed to help protect your walls from bumps and daily wear and tear. Durable materials such as wood and PVC are commonly used for these types of mouldings.
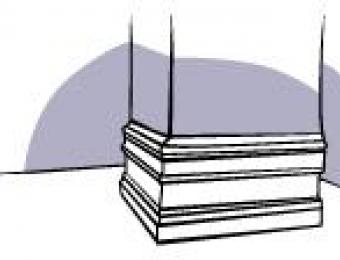
As plaster is quite brittle, bumps and knocks will weaken it over time and the mouldings will need to be replaced more frequently than those made from more hardy materials. For that reason, plaster is often used for ceiling mouldings. Plaster can be cast into complex shapes which means many ceiling mouldings (such as ceiling roses) are quite intricate. Ceiling roses are much cheaper when cast in PVC, however many people prefer to use plaster as it is more traditional and authentic. Plaster is made from naturally occurring minerals and is fire resistant.
How is plaster installed?
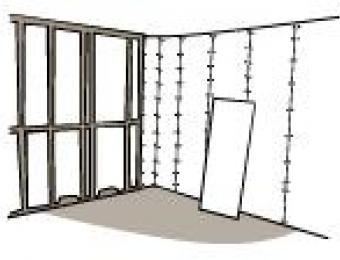
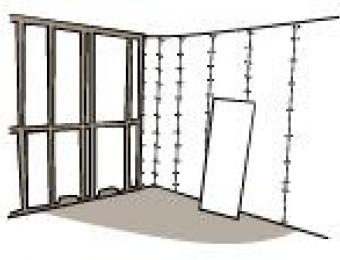
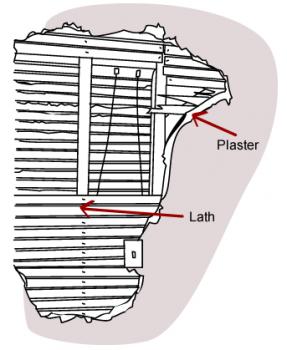
Plaster walls were traditionally made using strips of wood (called 'laths') with plaster spread over the top of them. As the plaster set, it would harden in the gaps between the wooden strips to hold the plaster in place.
Plaster mouldings are generally installed by nailing them to the wall studs. Care must be taken to ensure the corners of the horizontal strip moulding are adequately prepared so they fit together neatly. Ceiling roses and other ceiling mouldings are generally fixed to the ceiling using plaster adhesive and then nailed into place.
When using plaster to repair cracks or holes in walls, it's best to ensure that there is a solid backing to apply the plaster to. Once the appropriate amount of plaster has been mixed, it can then be smoothed onto the backing in a layer approximately 1 cm thick. Wet plaster generally requires 30 minutes to dry before a second layer can be applied. This process is repeated until the plaster is flush with the surface of the wall. Finally, the entire surface back is buffed gently with a fine grade sandpaper, then repainted, using a primer first.
Is plaster easy to maintain?
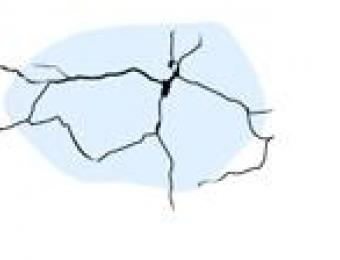
While plaster can crack and become brittle over time, it is such a common building material that it should be relatively easy to repair and replace.
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|