Climate control is at the very core of passive design - and ideally, your home should provide a comfortable, healthy environment in which to live. Striking a balance between a tight building envelope, naturally cool temperatures in summer and warmth in winter, good air quality, natural light and the many other variables that will affect your indoor environment can be quite a challenge.
Learn more about what needs to be taken into account if you're hoping to passively heat and cool your home.
What are R values?
R values are a way to assess how well thermal insulation works. Find out what's considered high and low where R values are concerned, and why there's more to insulation performance than just R values.
Insulation & passive design
Effective insulation plays a starring role in how well a house is able to separate the climate inside from that outside - and is therefore a critical part of passive house design and climate control.
Thermal bridges
Thermal bridges represent 'pathways' through your insulation along which heat can easily enter and escape from your home. These bridges can easily negate the benefits of good insulation, and must be carefully avoided.
Bulk vs. reflective insulation
Heat is gained in a home in a couple of different ways, and for that reason different types of insulation are needed for different purposes. Find out what the difference is between bulk and reflective insulation.
Efficient ventilation methods
The most effective ways to heat and cool your home are still with air conditioners and coolers - but carefully controlling ventilation can often prevent the need for them altogether.
Indoor air quality
The most important reason to ensure that your home is properly ventilated is to ensure that the quality of the air is not making you sick, and to avoid sick building syndrome.
How to measure infiltration and air tightness
Part of establishing how well your home fares in terms of passive design is to establish how 'tight' it is. Learn more about how to test how much air leaks from your home.
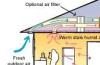
Heat recovery ventilators (HRVs)
Heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) and energy recovery ventilators (ERVs), while they do use energy, are an efficient and effective way to ventilate a tightly sealed home while maintaining the temperature.